Kolbe Wisdom
Next Generation  |
Innate Conative Strengths
|
Innate Conative Strengths  |
Action Modes |
Modus Operandi |
Three Zones Of Operation |
The Kolbe Index |
Predictable and Reliable |
12 Conative Strengths |
An Accurate Measurement of Conative Strengths Is Unbiased |
Self-Efficacy |
Full Capacity Being 100 Ergs |
Kolbe Creative Process |
Modus Operandi/Striving Instincts
|
Action Modes |
Modus Operandi |
Three Zones Of Operation |
The Kolbe Index |
Predictable and Reliable |
12 Conative Strengths |
An Accurate Measurement of Conative Strengths Is Unbiased |
Self-Efficacy |
Full Capacity Being 100 Ergs |
Kolbe Creative Process |
Modus Operandi/Striving Instincts  |
Dynamynd Of Decision Making |
Conative Stress |
Strain Or A Depletion Of Mental Energy |
Depletion |
Misidentified As ADD/ADHD |
Meltdown |
Conative Synergy |
Inertia |
Polarization |
Right Conative Fit |
Productivity Is Predicted
|
Dynamynd Of Decision Making |
Conative Stress |
Strain Or A Depletion Of Mental Energy |
Depletion |
Misidentified As ADD/ADHD |
Meltdown |
Conative Synergy |
Inertia |
Polarization |
Right Conative Fit |
Productivity Is Predicted
Copyright 2008 Kathy Kolbe. All rights reserved.
Next Generation – Audio (36 seconds) 
"Plato and Aristotle talked about this stuff. They said that there’s a cognitive, an affective and a conative element, and the conative element are the actions that lead to results. The cognitive are the thoughts that helps us come up with ideas the affect is the desire to do something but without the conative, the actions tied to instinct, there will never be a result. There’ll be no decision. There’ll be nothing that happens to get us where we need to go. So, throughout the ages we’ve know this has existed but the problem was always how do we measure it?"
 Click to listen to sound clip.
Click to listen to sound clip.
Kolbe, K. (Speaker). (2005). The Kolbe Creative Process/The Kolbe Concept [CD] Phoenix: Kolbe Corp. (36 seconds), 3:22 - 3:58
return to Knol | return to top
Innate Conative Strengths – Audio (52 seconds) 
"Your instincts aren’t like your social skills or your personality. These aren’t preferences, these aren’t things that you turn on and off. Your instincts are ever-present, always ready. They’ve been with you since you were born, and they’ll be with you throughout the rest of your life. They’re the gift God gave you. They are the internal strength and grounding point that you have. This is the core of you and it is so indelible, so much a part of everything you do that it’s like your DNA. It’s like your thumbprint. It’s what would be in the technical world, your hard wiring. This is you and there is nothing about this part of you that needs any alteration."
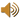 Click to listen to sound clip.
Click to listen to sound clip.
Kolbe, K. (Speaker). (2006). Your Kolbe Result/Your Instinctive Strengths [CD] Phoenix: Kolbe Corp. (52 seconds), 1:13 - 2:05
return to Knol | return to top
Action Modes®
"Energy from each striving instinct triggers a different set of actions. These lead to four consistent or characteristic ways of performing what we term Action Modes. Action Modes are the talents over which you have conscious control and which result in observable behavior.
These Action Modes define the abilities that link the internal force of instinct with quantifiable performance. They determine how you will, won't, and are willing to function, based on the necessities of your instinctive makeup.
You may know you should review your file notes before making a call, yet you usually fail to do so. You wish you would keep more organized records, but when you do, you can't find where you put them. What you should do will always be overpowered by a conflicting instinct-driven need."
Kolbe, K. (Jan. 2008) Kolbe Certification Manual Phoenix: Kolbe Corp.
return to Knol | return to top
Modus Operandi
"an unvarying or habitual method of procedure"
"Modus Operandi" http://dictionary.die.net/modus%20operandi
Modus Operandi (MO): A numerical representation of one's instinctive way of taking action as measured across the four Action Modes.
Kolbe.com (2008) http://www.kolbe.com/kc08/glossary.cfm Retrieved, February 2008
return to Knol | return to top
Three Zones of Operation
Fact Finder
Operating Zone Fact Finder Actions
Initiating Details, strategies, research
Responding With specifics, editing, assessing pros and cons
Preventing Analysis paralysis, or minutiae
Each zone indicates a differing degree of thoroughness necessary for an individual. Some people simply have to give you every detail of the movie plot. They are the ones who ask questions until they have the last piece of information, who operate with practical strategies based on historical evidence or personal experience.
Other people use information to satisfy someone else, responding with sufficient specificity yet not delving any more deeply than necessary into the details. For instance, they may wonder who is fourth, fifth and sixth in presidential succession. But for all their wondering, they won't search for the answer if they don't know it already. If a debate gets going over the issue, some people will need to cut off the discussion and move on to another topic. These people prevent situations from becoming immersed in specifics. Even if they raised the question-and find it interesting to consider-they'll get frustrated if the discussion gets bogged down in what they consider trivialities.
Follow Thru
Operating Zone Follow Thru Actions
Initiating Systems, procedures, design, order
Responding By adjusting to existing plans, maintaining classifications
Preventing Getting boxed in, being overly structured
Some people naturally put things into a system. They have an urge to straighten the picture, to flow-chart the options, and to organize people and materials. The first thing they do when faced with a problem is to sort out the possibilities. They take inventory of all the information accumulated by initiating Fact Finders.
Then there are those who will live within the system and follow the procedures. These accommodating Follow Thrus put things back where they belong. They may not need to have phone messages given to them in alphabetical order, but they will maintain such structures.
Those in the preventative zone in Follow Thru rebel when they feel boxed in by schedules or routines. They resist having to stay within the parameters of policies and procedures, and instead create their own alternatives. Sometimes their resistance to filling in the form can lead to open-ended comments that improve productivity.
Quick Start
Operating Zone Quick Start Actions
Initiating Change, deadlines, uniqueness
Responding By mediating between the vision and the given
Preventing Chaos, a crisis atmosphere
People who initiate Quick Start projects create the chaos that others have to clean up. But in the process these change makers add vision and risk to the mix. Always negotiable, they defy the odds and intuit possibilities that would otherwise go untried. Because they instigate the unusual, people who operate in the initiating zone of Quick Start are natural promoters and entrepreneurs.
Accommodating change is no problem for people who respond in Quick Start. For instance, they'll go along if you change your mind at the last minute and want to see a different movie.
Don't expect the same of those who operate in the preventative zone of Quick Start. They keep changes from getting out of hand, trying instead to reach agreement on what will stay the same. What some consider enhancements, they sense could cause a potential crisis. Their resistance to risk can save the day.
Implementor
Operating Zone Implementor Actions
Initiating Constructing, transporting, manipulating, and protecting tangible goods
Responding By using machinery or implements for either tangible or intangible effort
Preventing Need for tangible evidence or physical proof
Those who initiate solutions by using tools and implements are the hands-on Implementors. While others discuss the video they just saw, these folks are probably tinkering with the VCR. Their need for physical movement and space keeps them from staying in one place for very long. They tend to build solutions rather than talk about them.
People who respond through the Implementor mode are able to deal with both tangible and intangible solutions. If others need to put together a concrete demonstration they'll help build it, but they don't need to see the prototype in its final form in order to make a decision.
Prevention of Implementor action indicates an ability to create from abstract concepts such as words and numbers without having to use three-dimensional forms and models.
Kolbe, K. (1994-2004). Pure Instinct: The competitive advantage. Phoenix, AZ: Monuments Press. 16-19
return to Knol | return to top
The Kolbe A™ Index
"The Kolbe A index is a forced-choice instrument that requires subjects to choose one of four responses reflecting how they would most and least likely respond to 36 single-sentence problem-solving or behavioral scenarios. The raw scores reflect the frequency with which the subject would tend to initiate, respond to, or prevent probing, patterning, innovating and demonstrating behaviors. These frequencies are plotted on four ten-point scales that reflect the behavioral predispositions of the subjects. The scales are generally used in conjunction with each other to establish a pattern of individuals' overall predisposition, but each sub-scale can be used independently to focus on a particular pattern in a specific context."
Source: Kolbe works
Kolbe.com (2008), Kolbe A™ Index, Sample Result, page 2, Retrieved February 28, 2008 from http://www.kolbe.com/kc08/assessment-tools.cfm#kolbea
return to Knol | return to top
Predictable and Reliable
Test-retest Reliabilty
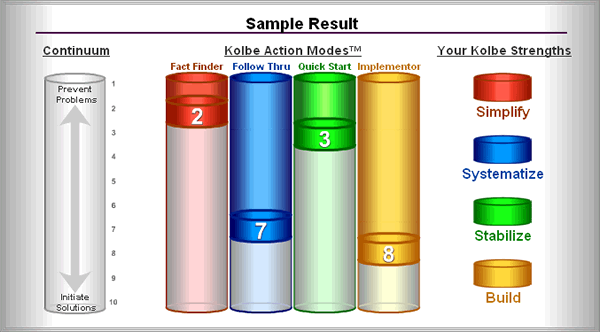
"One important aspect of understanding the strength of a test or instrument is its reliability. Test-retest reliability refers to the similarity of scores obtained by the same person who takes a test at two different times. A test that is reliable will result in few or no differences between the two test scores. The longer the time interval between testing is also an important consideration. Obtaining similar scores across a short time interval, less than a year for example, indicates test-retest reliability but longer intervals between tests helps to more rigorously examine its reliability. This study shows similarity of Index scores across relatively short intervals of 2 years up to lengthy intervals of up to 15 years."
Test-retest Reliability Study
"A study was completed to assess the test-retest-reliability of Kolbe A Index scores from 282 participants who had taken the Kolbe A Index at different times prior to July 2006. Subjects were contacted via email request to participate in a retest of the Index. Participation in the retest was voluntary, but most of the respondents took the initial Kolbe A Index as part of their employment. The retest data were gathered by the Center for Conative Abilities (a non-profit entity in Phoenix) between March and July of 2006."
Kolbe, K., Young, A. M., & Gerdes, K.A. (March, 2008). Striving instincts and conative abilities: The test-retest reliability of the Kolbe A™ Index. Annual Meetings of the Western Academy of Management, Oakland, CA.
return to Knol | return to top
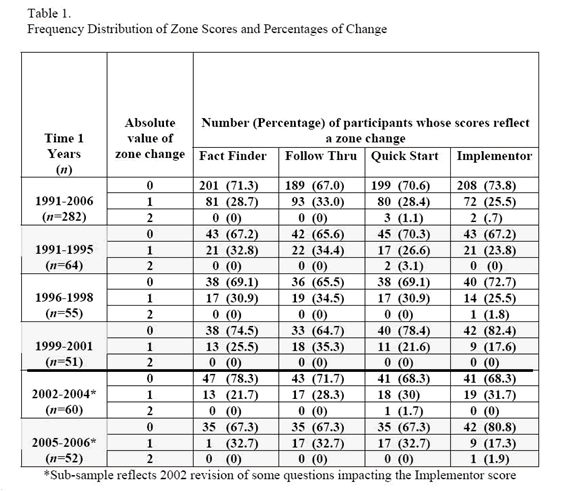
12 Conative Strengths
Kolbe.com (2008) http://www.kolbe.com/kc08/twelve-ways-to-solve-problems.cfm Retrieved, February 2008
return to Knol | return to top
An accurate measurement of conative strengths is unbiased by gender, race, and age.
"Dr. Robert T. Keim of the Decision Systems Research Center of Arizona State University conducted an extensive study of bias of the Kolbe instrument in 1990, in which he examined 4030 Kolbe results which were grouped into 17 groups reflecting common conative patterns similar to job selection criteria. Dr. Keim initially performed analyses of variance with each of the four conative instincts as dependent variables and race, gender and age as independent variables. In 65 of 68 analyses of variance the results showed that at the .05 level of significance that differences in scores on the Kolbe could not be attributed to the dependent variables of race, gender or age. For the three values where the initial analysis of variance did not provide conclusive results, a Chi Square analysis was conducted by computing a Chi Square base-model value for each with gender, race and age. Subsequent analyses of variance and Chi Square values were computed leaving out each of the independent variables. Comparisons between the base-model values and the subsequent values demonstrated that in no case do the independent variables of race, gender or age explain differences in scores. Dr. Keim concluded, 'We can conclude that at the Alpha=.05 level the Kolbe is not biased by gender, age or race.'"
Thomas, R. (February 18, 1998). Statistical Report on the Kolbe Indexes. Provo, UT: Brigham Young University
return to Knol | return to top
Self-Efficacy
"Self efficacy is commonly defined as the belief in one's capabilities to achieve a goal or an outcome."
Kirk,Karin (2008) Self-Efficacy: Helping Students Believe in Themselves http://serc.carleton.edu/NAGTWorkshops/affective/efficacy.html Retrieved Feb. 26 2008
Defining Self-Efficacy
"Self-efficacy provides a mechanism to explain individual behavior and may be defined as a person's perceived capability to perform a behavior. A high level of personal self-efficacy is associated with a positive self-concept and a self-appraisal of personal control and arises through experiences of mastery and the anticipation of competent performance. A person with a positive self-efficacy expects to succeed and will persevere in an activity until the task is completed. A person with low perception of self-efficacy anticipates failure and is less likely to attempt or persist in challenging activities. This individual has a negative self-concept and an expectation of incompetence or lack of control of actions and outcomes.
Self-efficacy varies in dimension of level, strength and generality (Bandura, 1982; O'Leary, 1985). Efficacious beliefs evolve from the individual's perception of competence in performing a behavior; inefficacious beliefs result from failing to meet personal performance expectations. The will power to persevere when met with obstacles is impacted by the person's confidence in achieving a behavior. Generality refers to the domains of functioning in which people judge themselves to be efficacious (O'Leary, 1985). Some experiences create situation-specific efficacy expectations, others develop a more generalizable sense of self-efficacy (Bandura, 1977a, 1997).
Existing scales to measure self-efficacy use indirect measurement of perceived level and strength of self-concept and self-actualization. Sherer, et al. (1982) developed a measure of general self-efficacy, while others test specific domains of functioning, including anxiety disorders (Bandura, 1977a, 1982), smoking cessation (Condiotte & Lichtenstein, 1981; DiClemente, 1981; Maher & Rickwood, 1997), childbirth (Drummond & Rickwood, 1997) and cancer prevention (see review by Lev, 1997). The researchers report strong content and construct validity for each of the tools developed to test a relationship between self-efficacy and likelihood to perform a behavior. Further testing across domains of functioning is needed to establish the generality of this concept."
Kear, Mavra (2000) Concept Analysis of Self-Efficacy http://www.graduateresearch.com/Kear.htm Retrieved Feb. 26 2008
Self-Esteem:
1. a realistic respect for or favorable impression of oneself; self-respect.
2. an inordinately or exaggeratedly favorable impression of oneself.
Dictionary.com http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/self-esteem Retrieved, February 2008
"Self-esteem deals with an individual's affective feelings about self-worth. Self-efficacy deals with the individual's freedom to use what is his or her own conative strengths."
Source: Kolbe lectures.
return to Knol | return to top
Full capacity being 100 ergs
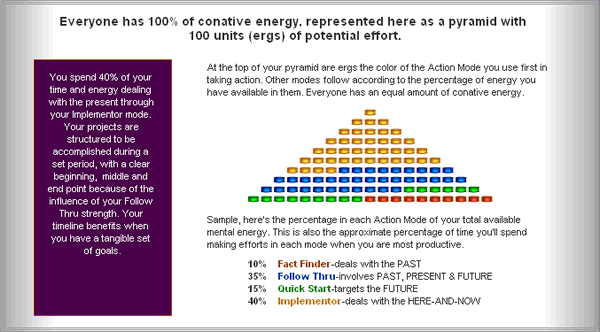
Kolbe.com (2008), Kolbe A™ Index, Sample Result, page 15 Retrieved February 28, 2008 http://www.kolbe.com/kc08/assessment-tools.cfm#kolbea
return to Knol | return to top
Kolbe Creative Process™ 
"The Kolbe Creative Process, which could also be called the Productivity Cycle, pinpoints when and how each element plays into the major adventures of the mind. Here's how it gets the job done:
1. Motivation, in the affective domain, is the catalyst. You have to want something to happen before you will focus your resources on it.
2. Instinctive energy is then engaged, with natural, conative talents focused on goals.
3. Free will commits instinctive drive to specific tasks.
4. Cognitive reason assesses possibilities, editing and evaluating any cross-purposes."
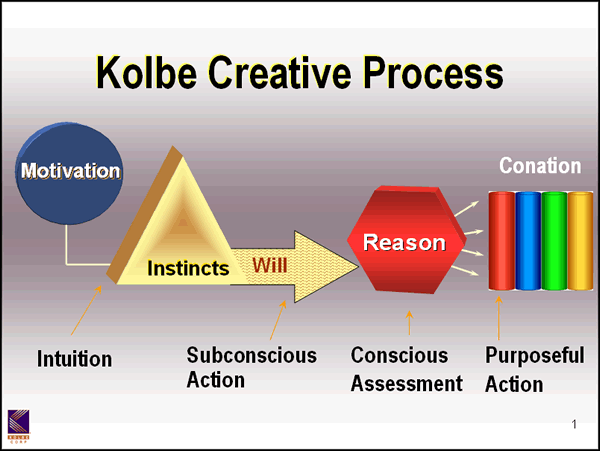
Kolbe, K. Kolbe Certification Manual Phoenix: Kolbe Corp. (Jan. 2008)
Modus Operandi/Striving Instincts - Audio (28 seconds) 
"The striving instincts are what I call those instincts that are necessary to the creative process. It has nothing to do with maternal instincts, or political instincts, or warring instincts, or fatal instincts. No, these instincts are the striving instincts, those energies we engage when we’re making decisions, solving problems, creating solutions. So, striving instincts are innate abilities or energies that we use when trying to reach a goal."
 Click to listen to sound clip.
Click to listen to sound clip.
Kolbe, K. (Speaker). (2005). The Kolbe Creative Process/The Kolbe Concept [CD] Phoenix: Kolbe Corp. (28 seconds), 6:02 - 6:30
return to Knol | return to top
Dynamynd® of Decision Making
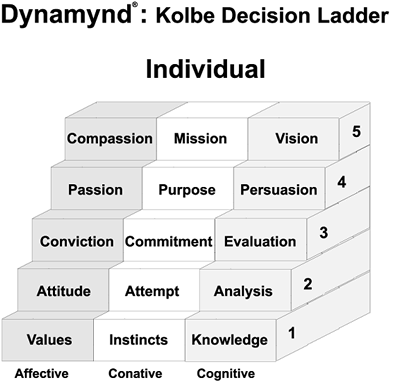
"Kathy: You need to match your conviction to make a difference with a commitment to do something that will make that difference. You need to be on the same step emotionally, conatively, and intellectually.
Ev: So in this example, I need to intellectually evaluate the effectiveness of different actions to see which ones will truly help the homeless person?
Kathy: Exactly. As you can see, the higher you go up the Dynamynd, the tougher the issues. But we can't just start at the top, especially if we've been ignoring our instinctive side! First we have to be self-aware to know what our values are and what makes us tick in terms of our natural MO, and to be sure of what we know vs. what we believe."
Kolbe, K. 2004 Powered by Instinct: Five rules for Trusting Your Guts Phoenix, AZ: Monumentus Press, 51-52
Dynamynd Decision Ladder: A hierarchical model of the graduated, sequential steps that lead to higher levels of thinking, feeling, and action taking in the creative problem solving process. Individual Dynamynd: A model of the specific behaviors an individual exhibits when making decisions at each level of the Dynamynd hierarchy, in each of the three dimensions of the mind: cognitive, conative, and affective. Culture Dynamynd: A model for assigning the status on the Dynamynd Decision Ladder for a category of people who are affiliated but who do not make decisions interactively. Team Dynamynd: A model of the levels of decision making - in all three dimensions of the mind - available to a group of people who work interdependently. Leader Dynamynd: A model of the levels of decision making required of leaders as they develop higher standards of performance for themselves and others whose decisions they influence.
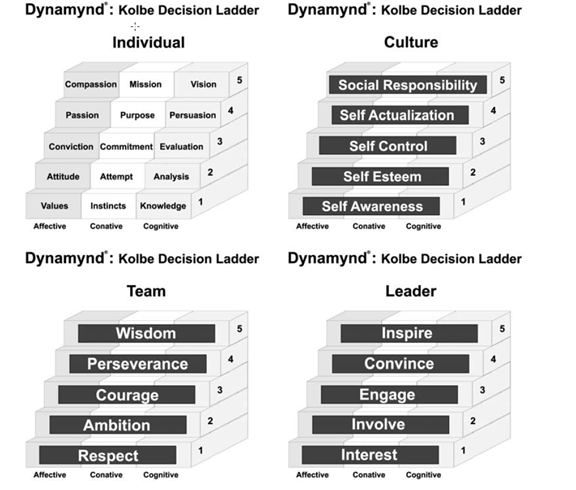
The Dynamynd clarifies how you have to go beyond simply having the amazing mental faculties found in the tripartite mind. It's a tool used to coach people on maximizing their use of these attributes. Your self-fulfillment and contribution to society can be tracked by assessing the levels you achieve in each of these aspects of your mental makeup. For instance, in the cognitive arena, you can build on knowledge by applying it, then stretch further to analyze information, evaluate it, and ultimately, to visualize its consequences. (See Bloom's taxonomy). I believe that a similar hierarchy influences your control over the affective and conative domains. To have a personality type is fine, but you need to understand how that leads to your preferences. Only then can you take responsibility for your values and develop a passion for what matters most to you. Many people stop short of developing a sense of passion. That keeps them at a very self centered level in the affective domain. While self-centered has a negative ring, it is the same as self actualization or self-fulfillment within the Dynamynd. This is a passage on the mental hierarchy for each domain, which is a necessary pathway toward development of leadership capabilities.
There are several ranges within the Dynamynd. If you aspire to make a difference in the world, to be socially responsible, you must pass through all of these levels. Only after a passion has shown up on your affective radar, can you arrive with a compassion for others. Only those who demonstrate this capacity become authentic leaders. Paralleling its mental siblings, the conative hierarchy begins with self awareness, a level which has been difficult to achieve without knowing your MO. Through your free-will, you can gain control over your use of this drive, directing it toward specific goals. Ultimately you could be acting on a mission that helps others. It's up to you to select the levels at which you choose to operate, and then to work to achieve them.
It is certainly possible to be at different points in each domain. Lucy, on the I Love Lucy show had a personal mission to get on Ricky's show. This was also her passion. On the cognitive side, she certainly didn't analyze the consequences of her actions, keeping her barely at level two.
Mother Teresa seemed to be at level five in all three domains. The Seinfeld team pulled off "a show about nothing," as was the stated goal. They maintained a mental "1" across the board. (By the way, that's tough to do. Just try not thinking about, caring about, or doing anything about anything significant!)
Source: The Writings of Kathy Kolbe
Kolbe, K. 2004 Powered by Instinct: Five rules for Trusting Your Guts Phoenix, AZ: Monumentus Press 220-222
return to Knol | return to top
Conative Stress
"Conative stress results when there's interference with the natural flow
of your instinctive power. It's triggered by:
- the strain of working against your grain
- the tension of efforts to fulfill another's requirement that you
operate contrary to your MO
- the natural conflict of working with someone whose instincts go
counter to yours"
Kolbe, K. 2004 Powered by Instinct: Five rules for Trusting Your Guts Phoenix, AZ: Monumentus Press
"Conative Stress is a difference of 4 or more units in any Action Mode"
Kolbe, K. (Jan. 2008) Kolbe Certification Manual Phoenix: Kolbe Corp.
return to Knol | return to top
Strain or a depletion of mental energy
"Strain: Condition where a person's sense of how a task needs to be performed is substantially difference from his/her natural methods of problem solving."
Kolbe, K. (Jan. 2008) Kolbe Certification Manual Phoenix: Kolbe Corp.
"1: an act of straining or the condition of being strained: as a: bodily injury from excessive tension, effort, or use <heart strain>; especially : one resulting from a wrench or twist and involving undue stretching of muscles or ligaments <back strain> b: excessive or difficult exertion or labor c: excessive physical or mental tension; also : a force, influence, or factor causing such tension <a strain on the marriage> d: deformation of a material body under the action of applied forces
"strain " Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary copyright © 2005 by Merriam-Webster, Incorporated http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/self-esteem (Retrieved Feb. 26 2008)
"Conative Stress: Conflict, Strain, and Tension...
...Conflict
When two people with contradictory instincts interrupt each other's progress by insisting on their own paths to problem solving, conflict occurs. Potential conflict is identified by comparing their Kolbe A index results (the individuals' conative realities). The potential for conflict exists when there is a difference of four or more units in an Action Mode.
It can lead to complementary synergy when both people enjoy the freedom to be themselves within the relationship, with neither attempting to impose his or her will on the other. Most successful teams are comprised of people who complement each other conatively. They bring differing talents to the table. By seeking outlets for talents that provide mutually beneficial results, conflict can foster complementary accomplishments. What one person avoids doing, the other may willingly contribute to the cause.
Prescription: humor, humility, trust, barter, respect, understanding, managing mental energy.
Strain
When an individual tries to live up to false self-expectations, the result is strain. Strain on the job is identified by comparing Kolbe A index results to Kolbe B™ index results (an individual's job-related self-expectations). A difference of four or more units in an Action Mode indicates the existence of strain. Strain is self-inflicted. It's caused by trying to "improve" in the Action Modes in which you are naturally resistant. Or trying to deny your own creative bent, it comes with trying to emulate someone conatively different from you, or yielding to pressure to be someone other than who you are. It can be as dangerous to your well-being as a blood transfusion of a mismatched natural type. It can keep you from fulfilling your destiny.
Prescription: acceptance, overcome guilt (good/bad or right/wrong), express creative self, change expectations, barter, outlets, confirm expectations as reality, targeting mental energy, trust.
Tension
When external obstacles posed by people or circumstances force an individual to work against his instincts, the result is tension. Tension is identified by comparing Kolbe A index results to Kolbe C™ index results (job requirements as determined by someone else-usually a boss or supervisor). A difference of four or more units in an Action Mode indicates the existence of tension.
Prescription: remove from situation, communication to change requirements, barter, manage mental energy.
Strain is the most difficult form of conative stress to allay. It stems from a betrayal of your own instincts and means that you are ignoring internal urges in favor of external rewards. It indicates an attempt to bypass your striving Instincts and act only according to detrimental motivations. Therefore it interferes with your Creative Process. A person suffering from strain limits her potential for success by not valuing, understanding, or using innate capabilities."
Kolbe, K. (2004). Powered by Instinct. (pp. 227-228). Phoenix, AZ: Monumentus Press
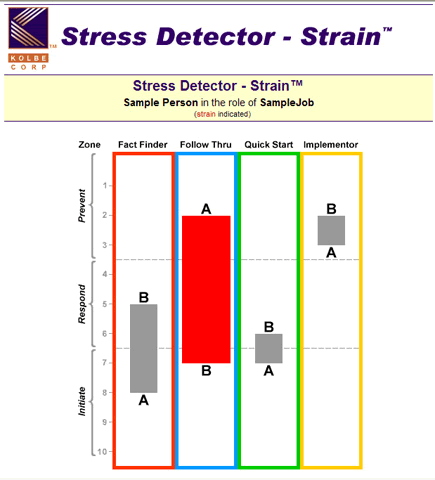
"Strain: A Form of Self-Denial
Denying your time-defined needs is the surest way to cause strain. For instance, a resistant Quick Start will be frustrated by the pressure of working against tight deadlines. Other sources of strain include:
1. Trying to live up to false self-expectations by:
- believing you can change who you are if you try hard enough
- confusing hard work with achievement
- undervaluing your ability to take action
- not recognizing a resistance as a strength
- attempting to rein in your instinctive impulses until you can rationally think things through
- thinking you aren't contributing unless you initiate action
2. Trying to live up to other people's expectations by:
- trying to do things the way you are told to do them
- trying to be just like someone you admire
- believing others know what is best for you
- promising you will do things differently
- taking criticism of your methods to heart
- knowing it annoys someone when you are just being yourself
3. Trying to function within the system by:
- trying to conform
- believing you can contribute best by altering your approach
- doubting what you have to offer is needed"
Kolbe, K. (2004). Powered by Instinct. (pp. 228-229). Phoenix, AZ: Monumentus Press
return to Knol | return to top
Depletion
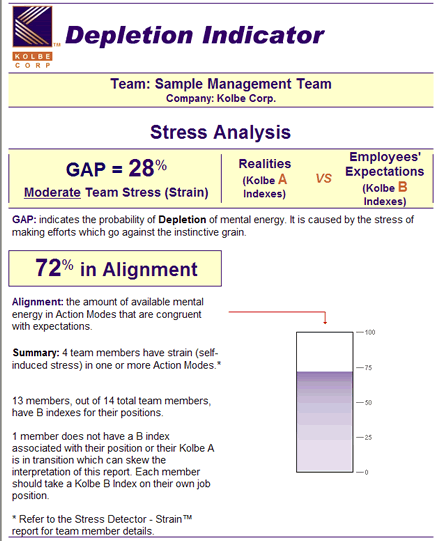
"Depletion is collective strain. When more than 15% of the team have strain in any one mode it becomes an organizational problem. 25% is a serious problem; 45% is disastrous.
Symptoms:
- Long hours, hard work, with little sense of accomplishment.
- Lack of job satisfaction
- Ill health
- Substance abuse
- Absenteeism
- Fatigue
Prescriptions:
- Team-building seminar to validate contributions
- Guidance in selecting appropriate methods-conative counseling
- Validating equality of talents and providing career advice"
Kolbe, K. Kolbe Certification Manual Phoenix: Kolbe Corp. (Jan. 2008)
return to Knol | return to top
Misidentified as ADD/ADHD
"Students who have the greatest distances from teachers in their conative patterns of action have a higher probability of being labeled ADD or ADHD than other students whose patterns of action are closer to that of teachers.
The group of teachers sampled had a greater need to be very orderly and are less inclined to accept interruptions than the students they teach.
- Two-thirds of the students labeled ADD/ADHD rank from 1-5 in Fact Finder, whereas two-thirds of the teachers rank from 6-10 in Fact Finder.
- Only 1 in 5 ADD/ADHD labeled students have innate traits that help them be consistent or even respond well to sequenced plans (a Follow Thru result of 6 or above), while most of the teachers have a natural need for such patterned efforts.
- More than half of the ADD/ADHD labeled students thrive on experimentation and spontaneity, a need that is exhibited by less than 30% of teachers (as measured by scores in Quick Start).
- About half of the students labeled ADD/ADHD have an inherent need for hands on learning (represented by a 6-10 score in Implementor). Less than one in five teachers show this need.
- Over half of the students who have not been labeled ADD/ADHD and nearly two-thirds of the teachers have a high need for Follow Thru systems (6-10 in Follow Thru), a need shared by less than one-fourth of ADD/ADHD labeled students."
Gerdes, K. & K. Kolbe (November 2006) Arizona State University Research on the Distribution of Conative Modus Operandi (MO) within Groups from the Same Classrooms, including Teachers, Students Identified as ADD/ADHD, and All Other Students
return to Knol | return to top
Meltdown
"Meltdown situations also lead to high rates of turnover and absenteeism. Stress-related illnesses have doubled in nine recent years, according to research conducted by Northwestern National Life Insurance Company. In three separate studies, instinctive strain and tension forecasted a doubling of turnover. The studies were conducted with corporations that had analyzed instincts, self-expectations, and requirements. In each situation the Kolbe Index-A and Kolbe Index-B results were given to employees but not placed in their personnel files. While senior management had the collective data relating to Depletion and Meltdown, the studies were done prior to most supervisors using the information. In all three companies, which were just beginning to study the benefits of using this approach, turnover within one year was at least 50 percent higher for employees suffering strain or tension than it was for other employees."
Kolbe, K. (1993) Pure Instinct NY: Random House/Times Books 160
return to Knol | return to top
Synergy
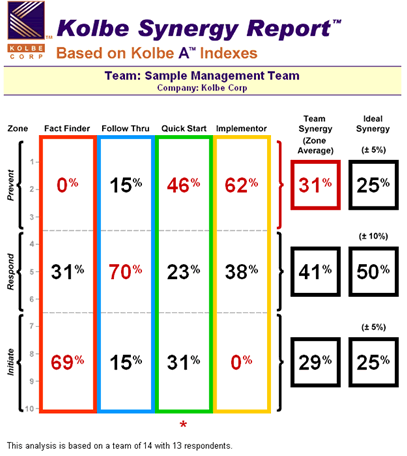
return to Knol | return to top
Inertia
INERTIA, THE CLONING OF CAPABILITIES
People on self-selected teams, who get to choose their coworkers, tend to select their instinctive clones-people with very similar MOs-unless they understand the implications of the Kolbe Concept®. When people's capabilities are redundant in a group, inertia sets in, and the team becomes passive. Even the loftiest goals won't stimulate such a sluggish group.
Kolbe, K. (1993). Pure Instinct. NY: Random House/Times Books. 146
.
return to Knol | return to top
Polarization
"Productivity is blocked when energy gets sidetracked in internal tugs-of-war. The wills and won'ts get so tangled up that management often resorts to feel-good seminars to try to get everyone working together. But sessions that make polarized groups feel better about each other don't have lasting benefits because the cause of the problem isn't resolved. Attitude adjustment is not the solution when a group is divided down the middle by conative needs. The solution can be found in project teams that bring in people who bridge differences in each Action Mode."
Kolbe, K. (1993). Pure Instinct. NY: Random House/Times Books. 154
return to Knol | return to top
Right Conative Fit
"Included in the Kolbe Wisdom™ is an integrated recruiting and selection program designed to fit within the framework of a company's existing methods of screening candidates for the necessary skills, experience, and attitude for a particular position. The centerpiece of Kolbe's process are diagnostic instruments that identify an applicant's inherent methods of creative problem solving (the Kolbe A Index or Kolbe S™ Index), the requirements of a position as determined by immediate supervisors and/or other evaluators (the Kolbe C Index), and the fit between the job requirements and the applicant's talents. This system provides organizations with a recruiting and hiring tool that is tailored to each job, quantifiably predictive of successful job performance, non-discriminatory, easy to administer and cost effective."
"The first step in the Kolbe RightFit™ program is the identification of a job's requirements. This step is crucial because it allows the organization to customize the recruiting criteria, instead of having an outside consultant come in and try to impose a one-size-fits-all approach. To accomplish this task, the people who will work with the potential hire complete Kolbe C Indexes that identify the job requirements. Each completed Kolbe C Index results in a profile of what the job requires in four categories of observable behavior patterns. In addition, where a position is replicated throughout an organization, Kolbe RightFit also takes into account the profiles of previous high performers in that job. Kolbe RightFit then analyzes the data collected from these various sources and computes a range in each category that corresponds to the necessary attributes as identified by the people who are most familiar with the requirements of the position (weighted toward the views of the direct supervisor). The resulting profile- or more precisely range of profiles- reflects the requisites for successful performance in the particular job, and is not the result of preconceived but unsupported notions of what qualities might be good in an applicant.
The next step in the Kolbe RightFit program is to identify the talents of the job applicants. This is accomplished through the administration of the Kolbe A Index or Kolbe S (Selection) Index, which are be scored with Kolbe WAREwithal® software. Once the instrument is scored, the Kolbe RightFit program compares the applicant's instinctive talents to those required by the job and provides a letter grade for each applicant on a sliding scale from 'A' through 'F.'"
Kolbe, K. (Jan. 2008) Kolbe Certification Manual Phoenix: Kolbe Corp.
return to Knol | return to top
Productivity Is Predicted
"The next study was completed by Dr. Richard S. Deems in January of 1992. He developed a Kolbe cut score for a national financial services company based on the profiles of successful managers. All 483 branch manager trainees hired in 1991 were divided into three approximately equal groups: 1) a control group which was not given the Kolbe, 2) a study group of trainees given the Kolbe whose scores fell outside the recommended range but whose managers were trained in conation to respond to the conative disconsonance, and 3) a study group of trainees whose scores fell within the recommended range. At the end of six months, 11.7% of the control group had left the company for job-related reasons, 5.5% of those who were conatively mismatched, but whose managers tried to mitigate the conative disconsonance by using the trainee's Kolbe results had left for job-related reasons, and none of the conatively-matched trainees left for job-related reasons."
Thomas, Ryan (February 18, 1998) Statistical Report on the Kolbe Indexes.
"Textron's fuel-systems division has utilized the Kolbe method for predicting how synergistic, and therefore productive, a team will be if it is managed in ways that encourage contribution of available talents. In one example, Van Kampen says a team that was stymied in reaching its goals was found to have sixty-six percent of its instinctive effort falling in the accommodation zone. Fifty percent is the ideal distribution; a team starts losing energy with a five-percent variation from that standard. So the fuel-systems group put in a person with two resistances and two insistences. Just one person-as identified by the Kolbe Index -changed the balance of the team and infused sufficient initiation and prevention to change the dynamics.
According to Van Kampen, "The group is now doing much better in terms of staying on schedule and making things happen. We've seen a real change. We can see an increase in the trust between people, especially on teams, and that is allowing us to shorten the lead times dramatically. It's a real competitive edge."
Kolbe, K. (2004) Pure Instinct NY: Random House
return to Knol | return to top
Copyright 2008 Kathy Kolbe. All rights reserved.
 |
Innate Conative Strengths
|
Innate Conative Strengths  |
Action Modes |
Modus Operandi |
Three Zones Of Operation |
The Kolbe Index |
Predictable and Reliable |
12 Conative Strengths |
An Accurate Measurement of Conative Strengths Is Unbiased |
Self-Efficacy |
Full Capacity Being 100 Ergs |
Kolbe Creative Process |
Modus Operandi/Striving Instincts
|
Action Modes |
Modus Operandi |
Three Zones Of Operation |
The Kolbe Index |
Predictable and Reliable |
12 Conative Strengths |
An Accurate Measurement of Conative Strengths Is Unbiased |
Self-Efficacy |
Full Capacity Being 100 Ergs |
Kolbe Creative Process |
Modus Operandi/Striving Instincts  |
Dynamynd Of Decision Making |
Conative Stress |
Strain Or A Depletion Of Mental Energy |
Depletion |
Misidentified As ADD/ADHD |
Meltdown |
Conative Synergy |
Inertia |
Polarization |
Right Conative Fit |
Productivity Is Predicted
|
Dynamynd Of Decision Making |
Conative Stress |
Strain Or A Depletion Of Mental Energy |
Depletion |
Misidentified As ADD/ADHD |
Meltdown |
Conative Synergy |
Inertia |
Polarization |
Right Conative Fit |
Productivity Is Predicted